Mental health is one of the major aspects that is greatly affected by drug abuse. The effect of drugs on the brain leads to disturbances in emotions, thinking, and memory. Therefore, this influence can be reflected in the individual’s behavior and in his relationships with others and with himself. Social disconnection and feelings of isolation are among the common consequences of drug abuse, as it can cause low self-confidence and deterioration in social relationships.
Furthermore, substance abuse can lead to an increase in mental health problems such as depression, anxiety, and psychosis. A person addicted to drugs becomes more vulnerable to psychological developments, and may find it difficult to deal with daily challenges properly. In addition, frequent drug use can lead to long-term mental health deterioration, increasing the chances of greater problems such as hallucinations and psychosis.
Individuals struggling with substance abuse must seek professional help to overcome the mental health challenges that arise from use. Psychological treatments, social support, and medical support can provide individuals with the essentials to recover and regain their mental health.

Addiction is a chronic health condition characterized by an intense expectation of drug use and the continuation of drug use despite the negative physical, psychological and social effects. Addicts are characterized by an inability to voluntarily stop using drugs, even when fully aware of the harm they cause. The disease of addiction can change the structure and function of the brain, making individuals more vulnerable to drifting toward destructive behaviors and harmful thinking.
The physical effects of addiction exacerbate health problems, as repeated drug use can cause damage to internal organs and deficiency of essential vitamins and minerals in the body. Addiction can also increase the risk of infectious diseases such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and viral hepatitis.
To overcome the disease of addiction, it usually requires specialized treatment and comprehensive support. Treatment to achieve success in recovering from addiction includes behavioral and drug therapy, and psychological and social support. Support groups and rehabilitative programs can also be helpful in promoting positive transformation and psychological and physical stability for addicted individuals.
Drug dependence is a condition characterized by an urgent and persistent need to use drugs in order to feel comfortable or to avoid the withdrawal that accompanies not taking them. Drug dependence can develop into a stage called “addiction,” where the individual becomes unable to control drug use voluntarily.
Cases of drug dependence require specialized treatment and comprehensive support to get rid of them. Treatment can include the provision of pharmacological treatments that help manage withdrawal and reduce desire to use drugs, as well as psychosocial support provided by doctors, counselors, and support groups.

Stopping drug use requires strong will and professional support. The person should start seeking help by searching for specialized treatment programs that suit his or her individual needs. These programs can include cognitive behavioral therapy, life skills training, and individual and group psychological support.
In addition, a person must work to change his usual lifestyle and think positively. Exercising, healthy nutrition, and acquiring new hobbies can help strengthen determination and maintain psychological stability.
Furthermore, a person should look for strong social support from friends, family, and community. Interacting with people who support positive change and encourage engagement in alternative healthy activities can be beneficial to help stay on track.
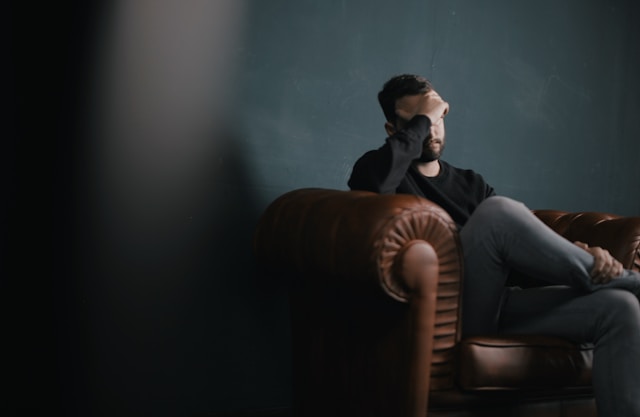

Common signs of abuse can include behavioral, psychological, and physical changes that appear in an individual as a result of drug use. These changes include severe mood swings, withdrawal, and aggression, in addition to changes in academic or work performance and social engagement.
On the physical side, signs may include sudden weight loss, abnormal overall appearance, red eyes, physical tremors, and strange breath. These signs should raise concern and prompt immediate intervention to help the affected individual.
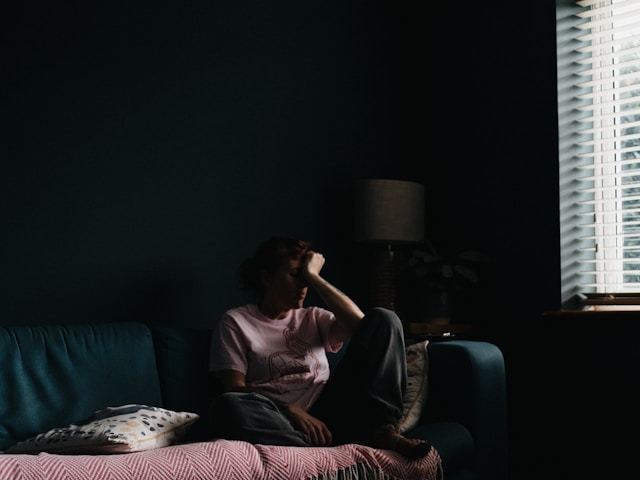

Children and youth are exposed to many social and psychological pressures that may push them towards experimenting with drugs. These include a desire to be bullied or belong to certain groups, stress from family problems, and curiosity about trying new things.
In addition, environmental factors can play an important role in encouraging youth use, such as the availability of drugs in the community, youth-oriented advertising marketing, and acceptance of the culture of use in some communities.

Opportunities for drug use are influenced by many factors, including an individual's social, economic, and cultural environment. Good family guidance and proper upbringing are one of the most important preventive factors that can reduce the chances of drug abuse. Health awareness and education about the risks associated with drug use can also play an important role in reducing the drift toward this harmful behavior.
On the other hand, some risk factors such as psychosocial stress, lack of social affiliation, and exposure to physical or emotional abuse can increase the likelihood of drug use. Communities, families, and government agencies must work together to provide a supportive and stimulating environment for individuals to help them overcome these obstacles and avoid drug use.
All rights reserved to Afaq Alwiqaya